Wildlife Conservation Day: How E-Waste is Impacting Wildlife Worldwide
Wildlife Conservation Day on December 4th is a reminder to protect animal species and their habitats. Often, we think of wildlife conservation in terms of protecting forests, oceans, or endangered species. But there’s an often-overlooked threat affecting ecosystems globally: e-waste. We live in a time of fast technology changes. Because of this, electronic waste, or e-waste, is a big environmental issue. This problem is especially serious in areas where wildlife is already in danger.
In this article, we’ll explore how e-waste impacts animals, what happens when electronics are not disposed of responsibly, and the steps we can all take to help wildlife thrive. By understanding the relationship between e-waste and wildlife, we can make smarter choices to protect the environment.
What is Wildlife Conservation Day?
Wildlife Conservation Day was created to raise awareness about the problems wildlife face worldwide. These problems include poaching, habitat destruction, and climate change. It’s a day for individuals, organizations, and governments to come together to discuss solutions for wildlife preservation. From elephants in Africa to coral reefs in Australia, wildlife conservation efforts are crucial in maintaining biodiversity and protecting ecosystems that humans also rely on.
This day encourages everyone to take steps toward conserving habitats and advocating for policies that protect wildlife. Now, with the rising threat of e-waste, conservation has expanded to include proper electronic disposal methods, an area not traditionally associated with wildlife but one that poses severe risks.
How Does E-Waste Affect Wildlife?
Pollution of Soil and Water Sources
E-waste contains toxic chemicals like lead, mercury, and cadmium. Improperly discarding old electronics releases harmful substances into soil and water. These pollutants impact animals, especially those dependent on clean water sources like rivers and streams. Toxins from e-waste not only contaminate drinking water but also enter the food chain, affecting animals at all levels.
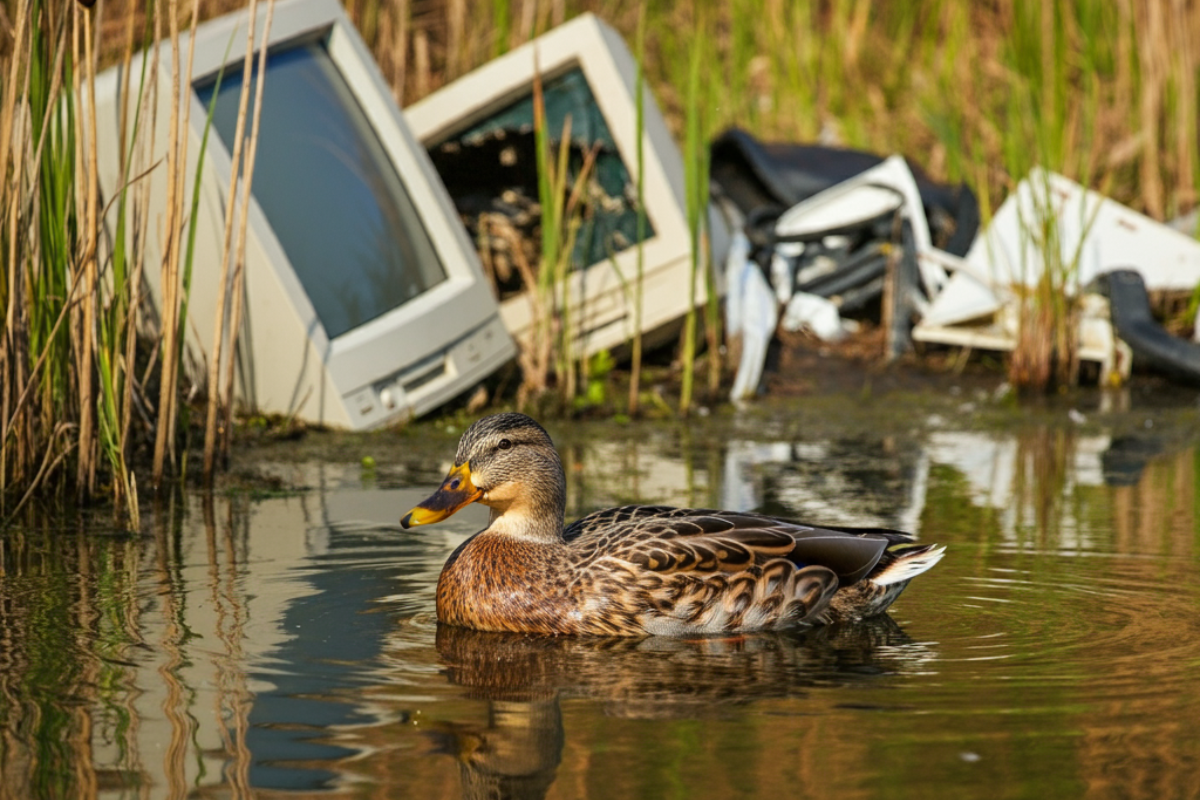

Habitat Destruction Due to E-Waste Dumping
Improper disposal of e-waste can lead to significant habitat destruction. Many electronics are shipped to developing countries where there are fewer regulations for waste processing. These areas often become dumping grounds, displacing wildlife and threatening native species. Animals are either forced to relocate or face harm as their habitats are taken over by waste processing activities.
Health Risks to Animals from E-Waste Exposure
E-waste doesn’t just harm animals indirectly—it also affects their health directly. Animals exposed to e-waste might suffer from respiratory issues, organ damage, or reproductive issues due to chemical exposure. Studies have found that animals living near e-waste dumps show higher levels of toxic substances in their bodies, which can shorten lifespans and lower population numbers.
How E-Waste Could Worsen Without Action
The impact of e-waste on wildlife will only increase if we don’t address it now. A study by UC Irvine highlights the pressing nature of this issue. Researchers believe that we need to improve our management and recycling of electronics.
If we don’t, e-waste could lead to 852 million metric tons of CO2 emissions each year by 2030. This will worsen climate change and put wildlife at greater risk. Many animals are already struggling to adapt to warmer temperatures and changing ecosystems.
Without strong regulations, e-waste pollution will keep growing. This will harm habitats and raise health risks for animals everywhere. With more digital devices being produced each year, it’s essential to address e-waste for both environmental and wildlife conservation.
What You Can Do to Help on Wildlife Conservation Day
If you’re passionate about protecting wildlife, Wildlife Conservation Day is a great time to take action. Here are some ways to get involved:
Recycle or Donate Electronics
Instead of throwing out your old devices, consider recycling them or donating them to certified e-waste recyclers. Electronics recycling companies ensure that the harmful chemicals in electronics are handled responsibly, keeping them out of wildlife habitats.
Buy Refurbished Electronics
Purchasing refurbished electronics instead of new ones helps reduce demand for new devices and the environmental impact of manufacturing. Refurbished items are just as reliable, and this option lessens the amount of e-waste generated overall.
Support E-Waste Legislation
Advocating for stronger e-waste disposal regulations can make a difference. Many regions lack the proper frameworks to manage e-waste, so supporting legislation that regulates e-waste disposal and recycling helps protect the environment and, by extension, wildlife.

Raise Awareness on Social Media
Share information about the impact of e-waste on wildlife on platforms like Instagram, Facebook, or Twitter. Use Wildlife Conservation Day as an opportunity to educate others about the importance of responsible electronics disposal and inspire them to take similar steps.
Reduce Personal E-Waste
Before upgrading to a new device, consider whether you genuinely need it. By extending the life of your current gadgets, you can reduce the e-waste you generate and lessen the demand for new products that often end up harming the environment. You can do this by going to local stores or nearby certified recyclers to recycle your electronic devices.
Living Sustainably
Wildlife Conservation Day is a time to reflect on how our actions affect the world’s animals. E-waste, although commonly overlooked, is a growing threat to ecosystems and the species that inhabit them. By understanding the impact of electronic waste on wildlife, we can take meaningful steps to reduce our environmental footprint and protect animals.
Recycling your old devices, supporting better e-waste laws, or sharing information on social media all make a difference. Wildlife Conservation Day is a reminder that preserving nature isn’t just about protecting animals directly—it’s also about minimizing our impact on their homes and resources.